5 Advantages to Using SVG Files
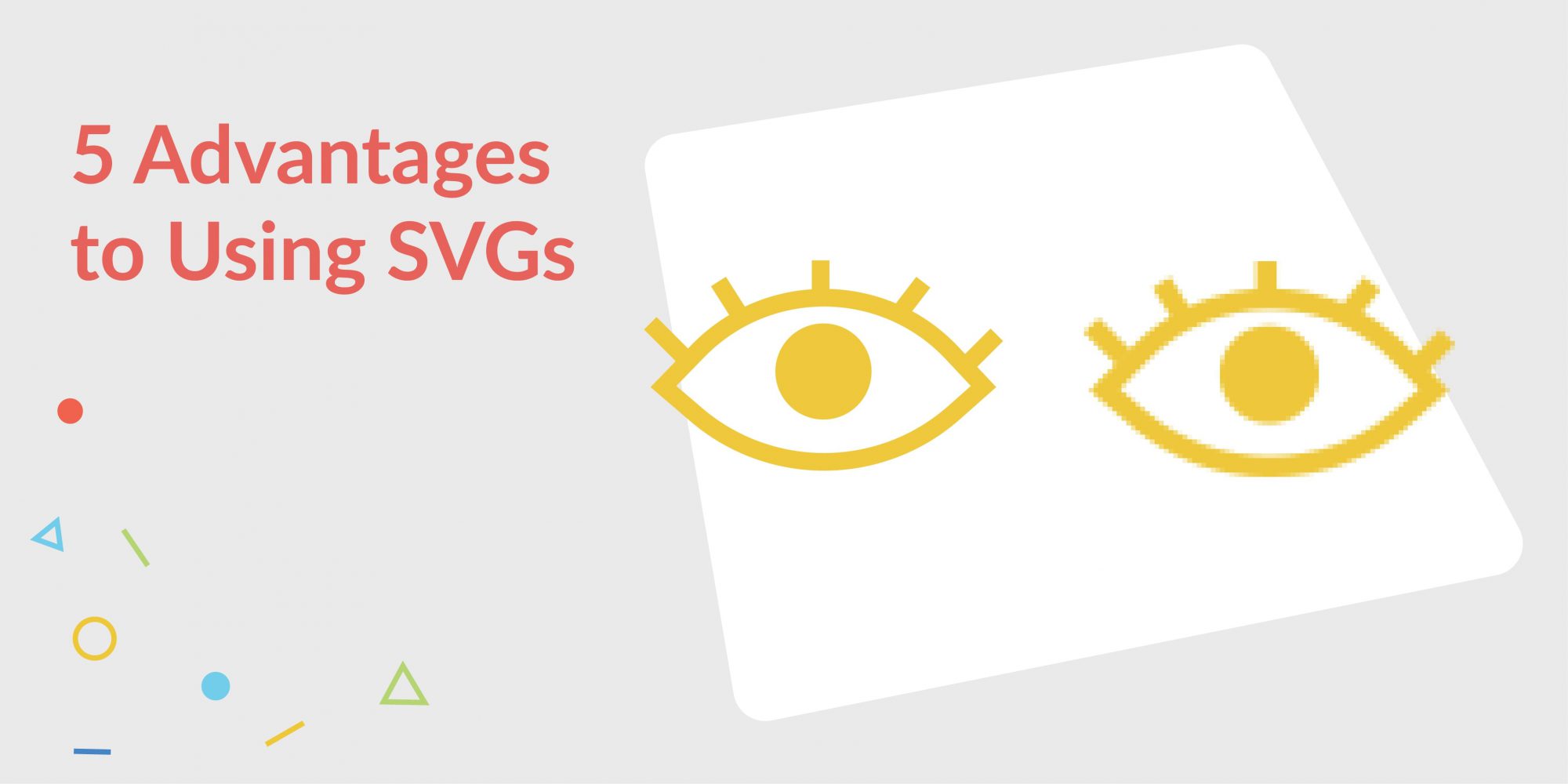
The variety of devices, screen sizes, and display resolutions makes quality scalability and responsiveness essential in providing your digital audience with an optimal experience. Some images may look fine at first glance, but as viewers start zooming in, they may begin to wonder if they need to grab their reading glasses to clear up the emerging blurriness. If you aren’t using Scalable Vector Graphics (SVGs) yet to avoid this problem, read on.
There are two major types of two-dimensional digital graphics used – raster and vector. Raster images, or bitmaps, are composed of a fixed set of tiny dots or pixels. Some of the basic file types include JPG, GIF and PNG. SVGs are vector images which are composed of mathematical equations where lines and curves (or paths) make up graphic shapes, images, and text in XML format. Although SVGs have been around a long time and offer several advantages, they are still an underutilized format in design.
SVG is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). According to the W3C, even in the early days of the web, it was apparent that a vector graphic format would be useful. Although it was influenced by ideas and specifications from submissions from several top companies, The W3C basically designed SVG from the ground up. They offer several advantages over raster images, including:
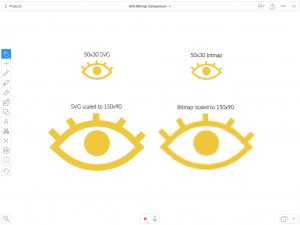
- Scalability – Vector images are resolution-independent and can scale to any dimension without losing quality. Browsers just recalculate the math behind the image so there is no distortion. Raster images on the other hand lose their resolution when enlarged because their small pixels are forced to expand beyond their original size.
 Interactivity – Hyperlinks and virtually any kind of animation can be added via styling and scripting.
Interactivity – Hyperlinks and virtually any kind of animation can be added via styling and scripting.- Easily editable – Editing an SVG is as easy as changing the coordinates or a word in a text editor or coding the SVG onto your webpage and altering it with JavaScript or CSS. You can also use popular vector graphics editing software such as Adobe Illustrator, Corel Draw, and Sketch.
- Compact file-size – Pixel-based images are saved at a large size from the start because you can only retain the quality when you make the image smaller, but not when you make it larger. This can impact a site’s download speed. Since SVGs are scalable, they can be saved at a minimal file size.
- SEO friendly – SVG images are defined in XML text files, so key words and descriptions can be used and more easily recognized by search engines. With raster images, you are limited to the title or alt attribute of your file.
As the quality on displays continues to increase on our devices, so must the images that we see. Although raster remains the preferred choice for photographs (because of their deep color depth), SVGs are ideal for illustrations like logos, icons, and graphs. Their infinite scalability makes them aesthetically pleasing, especially on platforms that provide an infinite digital canvas to work on.

